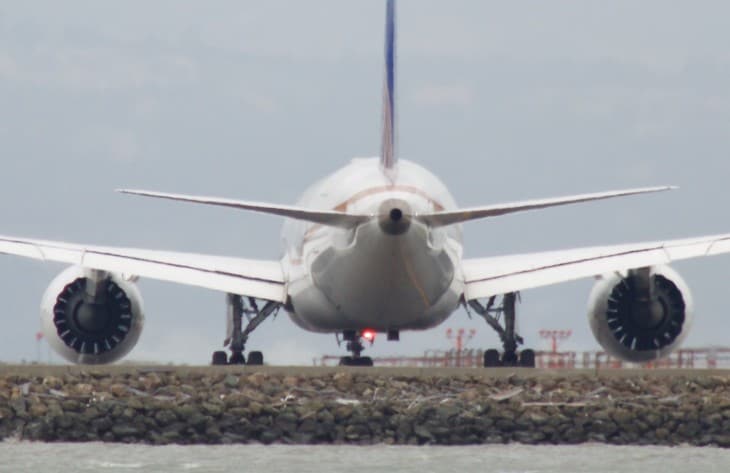
The positioning of airplane engines is a fundamental aspect of aircraft design, significantly impacting performance, efficiency, and safety. In modern aviation, most commercial airplanes feature engines mounted under the wings, a design choice driven by multiple technical and practical considerations.
Early aircraft designs were vastly different from today’s models, with engines often placed in various positions, including the nose or body of the plane. These early designs were largely experimental, focusing on achieving flight rather than optimizing performance or efficiency.
As aviation technology advanced, designers began to recognize the impact of engine placement on the aircraft’s overall aerodynamics and stability. The transition to engines under the wings marked a significant evolution in aircraft design, aligning with advancements in aerodynamics and propulsion technology.
This shift was driven by the need for larger engines to power bigger, faster planes, necessitating a reconsideration of traditional engine placement strategies.
6 Reasons Why Airplane Engines Are Under The Wing
Airplane engines are typically placed under the wings for several key reasons:
- Aerodynamic Efficiency: Placing engines under the wings can help with the aerodynamic efficiency of the aircraft. This position helps in reducing drag and improving the lift-to-drag ratio, which is crucial for efficient flight.
- Structural Balance and Stability: Mounting engines under the wings helps balance the aircraft’s center of gravity. This position also aids in maintaining the structural integrity of the aircraft, as the wings provide a strong, stable platform for the engines.
- Maintenance and Accessibility: Engines mounted under the wings are generally more accessible for maintenance and inspection compared to other positions like the tail or the fuselage. This accessibility can lead to more efficient and quicker maintenance operations.
- Noise Reduction: Positioning engines under the wings can help direct noise away from the cabin, contributing to a quieter passenger experience. This placement can also be beneficial in reducing noise pollution on the ground.
- Safety in Case of Engine Failure: In the event of an engine failure, having the engines under the wings can help in maintaining better aircraft control. The position allows for more balanced aerodynamics and helps prevent the aircraft from rolling or yawing excessively.
- Fuel Efficiency: The placement under the wings can also contribute to fuel efficiency. This is partly due to improved aerodynamics and also because the weight of the fuel in the wings helps balance the weight of the engines, reducing the stress on the aircraft’s structure.
Each of these factors plays a role in the common design choice of mounting engines under the wings of most commercial airplanes. This design has been found to be effective in balancing the various technical, operational, and safety considerations involved in aircraft engineering.
Aerodynamics of Wing Placement
Aerodynamics plays a crucial role in aircraft design, influencing speed, fuel efficiency, and stability. Wing placement affects the aircraft’s center of lift, a critical factor in maintaining balance and stability in flight. Integrating engines under the wings contributes to this aerodynamic balance, enhancing lift and reducing drag.
This placement allows for more streamlined airflow over the aircraft body, improving overall aerodynamic efficiency. Additionally, under-wing engines contribute to the lift generated by the wings, further optimizing aircraft performance.
Advantages of Under-Wing Engines
Positioning engines under the wings offers several advantages. Firstly, it improves fuel efficiency by reducing aerodynamic drag and balancing the aircraft’s weight distribution.
This placement also aids in noise reduction, as the wings partially shield engine noise from the cabin and the ground. Maintenance accessibility is another significant benefit, as under-wing engines are easier to inspect and service compared to other positions.
Furthermore, this design minimizes the risk of foreign object damage, as engines are elevated off the ground, away from debris on runways or taxiways.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite its advantages, under-wing engine placement also presents certain challenges. Structural considerations are paramount, as the wings must be reinforced to support the weight and vibrations of the engines.
Ground clearance issues can arise, particularly with larger engines, requiring careful design to prevent contact with the ground during takeoff, landing, or taxiing.
Balancing these factors is a complex task, requiring precise engineering and design optimization to ensure safety, performance, and efficiency.
Engine Placement in Bush Planes
Typically, bush planes have high-wing designs with engines mounted on the wings or, in some cases, a single engine mounted on the nose. The high-wing design is advantageous for bush planes because it provides excellent visibility below the aircraft, which is crucial for bush pilots navigating in remote areas.
Additionally, the high-wing configuration keeps the engine(s) away from ground debris, a significant concern when operating on unimproved runways.
The nose-mounted engine configuration, common in many bush planes, simplifies the design and maintenance. It also aids in effective weight distribution and balance, especially important for aircraft that frequently operate from short and uneven runways.
In multi-engine bush planes, engines are still often mounted under the wings, but the high-wing design helps in keeping them clear from ground obstacles and debris.
Bush planes are engineered for superior low-speed performance and maneuverability, necessary for flying in and out of confined areas. The engine placement plays a role in achieving the desired lift and thrust characteristics, enabling these planes to operate efficiently under challenging conditions.
Future Trends and Innovations
Aircraft design is continually evolving, with emerging trends and innovations shaping the future of engine placement. Advances in materials science and propulsion technology may lead to new configurations, potentially revisiting other engine positions or introducing novel designs. Environmental considerations, such as reducing emissions and noise pollution, are also driving innovation in engine and aircraft design.
Related Posts